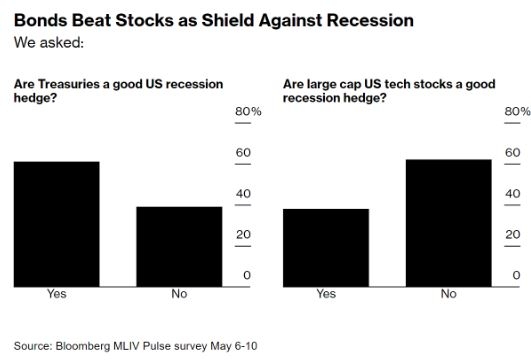
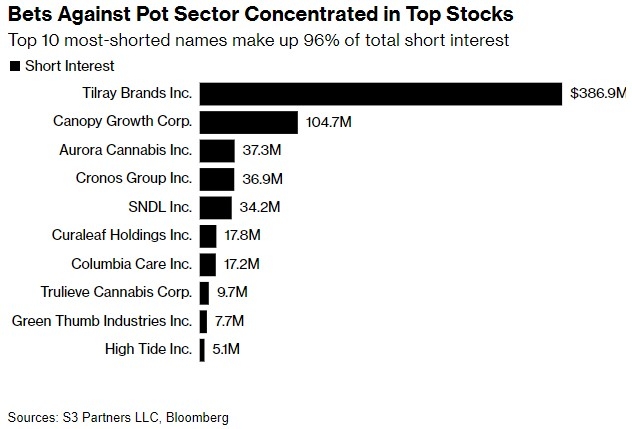
Title: Is the US Stock Market Efficient?
author:US stockS -
Introduction: The United States stock market has long been a beacon of financial opportunity and stability. With a rich history and a diverse range of companies, it has attracted investors from all over the world. However, one burning question that often comes up is whether the US stock market is efficient. In this article, we will delve into this topic, examining the different aspects of market efficiency and providing insights into the current state of the US stock market.
Understanding Market Efficiency: Market efficiency refers to the degree to which stock prices reflect all available information. In an efficient market, stock prices adjust quickly and accurately to new information, making it difficult for investors to consistently achieve above-average returns.
Types of Market Efficiency: There are three types of market efficiency: weak, semi-strong, and strong.
Weak Form Efficiency: This form of efficiency suggests that stock prices already reflect all historical price and volume information. As a result, technical analysis is unlikely to provide an edge in predicting future price movements.
Semi-Strong Form Efficiency: In addition to historical data, this form of efficiency incorporates all publicly available information, including financial statements, news, and economic reports. This implies that fundamental analysis is also unlikely to provide an advantage.
Strong Form Efficiency: This is the highest level of efficiency, where all information, public and private, is already reflected in stock prices. In this case, even inside information would not provide an advantage.
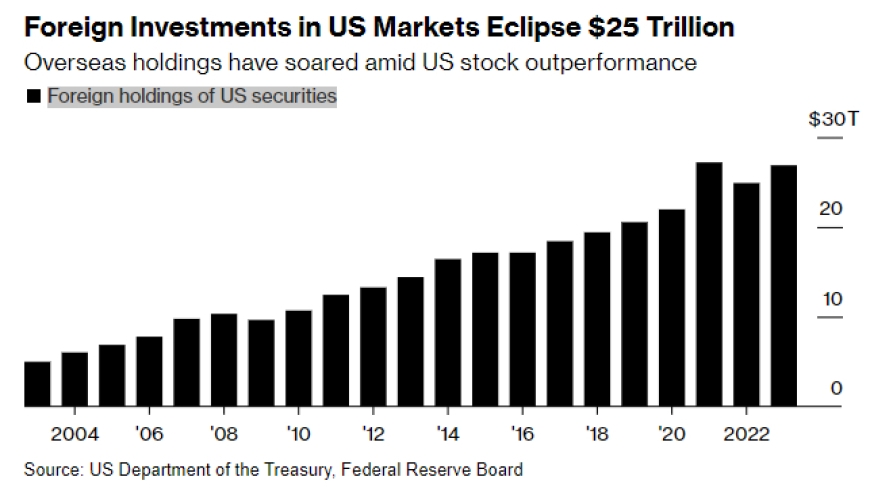
Current State of the US Stock Market: The US stock market is often considered to be semi-weakly efficient, meaning that while it incorporates historical price and volume information, it may not fully incorporate all publicly available information.
Challenges to Market Efficiency:
Information Asymmetry: This occurs when one party has more or better information than others. For example, corporate insiders may have access to private information that is not available to the public.
Market Manipulation: Unethical practices, such as insider trading and market manipulation, can distort prices and make the market appear less efficient.
Market Psychology: Investor sentiment and behavioral biases can also affect stock prices, leading to market inefficiencies.
Case Studies:
Enron Scandal: The collapse of Enron in 2001 highlighted the risks of information asymmetry and market manipulation. The company's executives engaged in fraudulent accounting practices, leading to a significant loss for investors.
Facebook IPO: The Facebook IPO in 2012 was criticized for its handling of the offering, raising questions about the market's ability to efficiently price initial public offerings.
Conclusion: While the US stock market is often considered to be efficient, it is not without its challenges. Information asymmetry, market manipulation, and investor psychology can all contribute to market inefficiencies. As investors, it is crucial to be aware of these factors and to conduct thorough research before making investment decisions.
us stock market today live cha