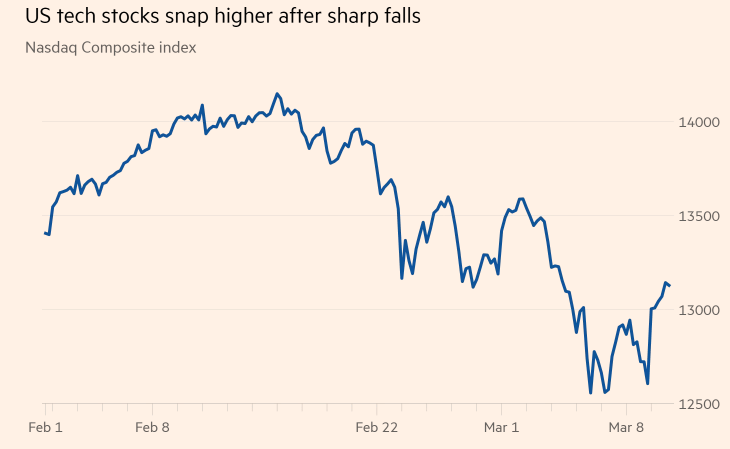
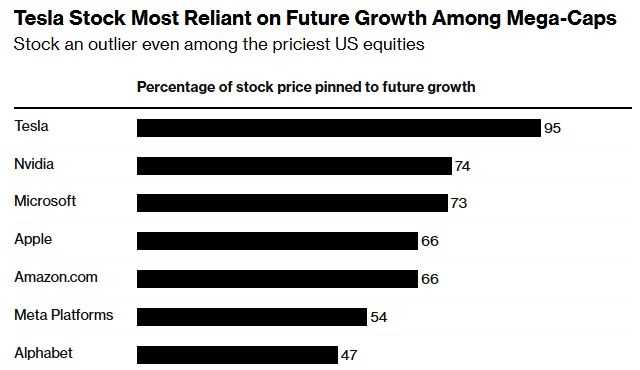
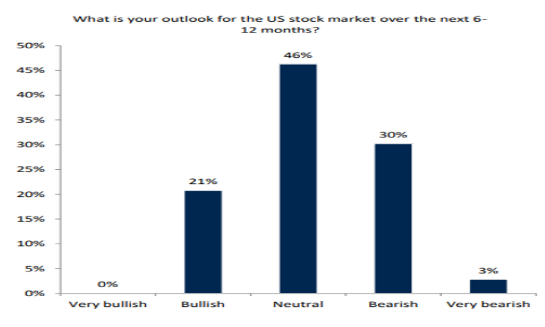
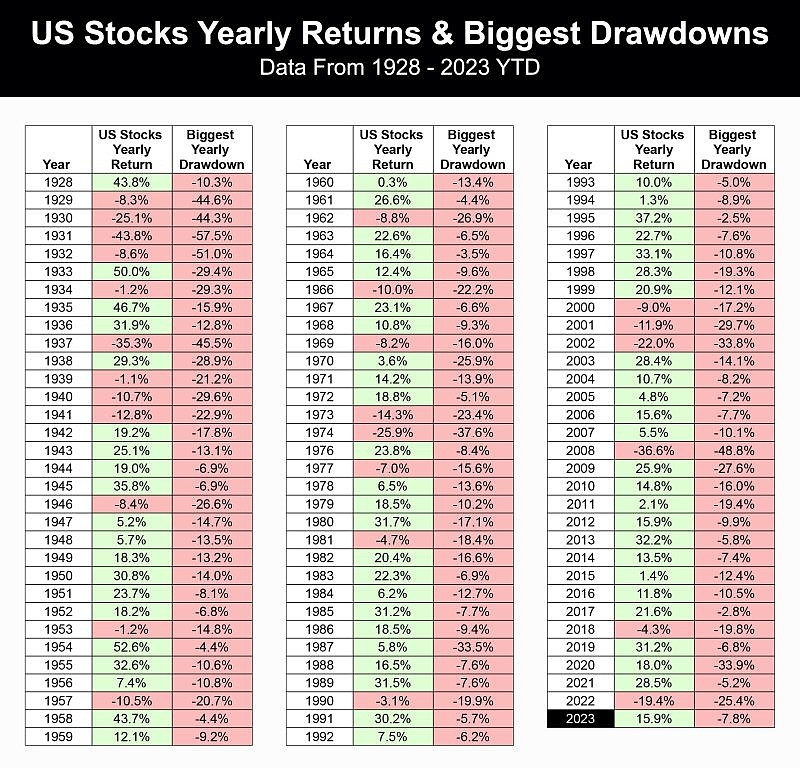
Statistics: U.S. Stock Market Monthly Outflow
author:US stockS -
The U.S. stock market has long been a beacon of economic activity and investment opportunity. However, recent trends have shown a concerning shift: a monthly outflow of capital. This article delves into the statistics behind this trend, exploring the factors contributing to the outflow and their potential implications for the market.
Understanding Monthly Outflow
Monthly outflow refers to the amount of money investors withdraw from the stock market over a given month. This statistic is crucial for understanding investor sentiment and market trends. In recent years, the U.S. stock market has experienced a notable outflow, raising questions about investor confidence and market stability.
Factors Contributing to Outflow

Several factors have contributed to the monthly outflow from the U.S. stock market. Economic uncertainty, political instability, and market volatility are among the key drivers. Additionally, increased interest rates have made alternative investments more attractive, leading investors to withdraw from stocks.
Economic Uncertainty
One of the primary reasons for the outflow is economic uncertainty. Global economic conditions, including trade tensions and geopolitical conflicts, have created a volatile environment that discourages long-term investments. Investors are becoming increasingly cautious, seeking safer investments or withdrawing capital altogether.
Political Instability
Political instability also plays a significant role in the outflow. Recent political events, such as elections and policy changes, have created uncertainty and anxiety among investors. This uncertainty leads to increased volatility and, ultimately, outflows from the stock market.
Market Volatility
Market volatility is another critical factor contributing to the outflow. Rapid and unpredictable changes in market conditions make it difficult for investors to predict future trends. This uncertainty leads to increased risk aversion and outflows from stocks.
Interest Rates
Increased interest rates have also played a role in the outflow. As interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, making alternative investments, such as bonds, more attractive. This shift in investor preferences leads to a withdrawal of capital from the stock market.
Implications for the Market
The monthly outflow from the U.S. stock market has significant implications for the market's future. A sustained outflow could lead to a bear market, characterized by falling stock prices and increased volatility. However, it's important to note that outflows are not always indicative of a market downturn. In some cases, they can be a sign of healthy market adjustments.
Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of monthly outflow, let's consider a few case studies. In 2018, the U.S. stock market experienced a significant outflow as investors became concerned about economic uncertainty and market volatility. This outflow led to a brief bear market before the market recovered. Similarly, in 2020, the stock market experienced a massive outflow during the COVID-19 pandemic. The market eventually recovered, but the outflow was a clear indicator of investor sentiment at the time.
Conclusion
The monthly outflow from the U.S. stock market is a concerning trend that reflects investor uncertainty and market volatility. While it's important to monitor these statistics, it's also crucial to consider the broader economic and political context. Understanding the factors contributing to the outflow can help investors make informed decisions and navigate the changing market landscape.
us stock market live