Difference Between Us Stock Markets and Japan
author:US stockS -
Introduction
When it comes to global stock markets, the United States and Japan are two of the most prominent players. Both markets offer unique opportunities and challenges for investors. Understanding the differences between these markets can help investors make informed decisions. In this article, we will delve into the key distinctions between the US stock markets and Japan, covering factors like market structure, investor sentiment, and regulatory frameworks.
Market Structure
The US stock market is characterized by its diverse range of exchanges, including the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), the NASDAQ, and regional exchanges like the American Stock Exchange (AMEX). This diversity allows for a wide array of investment options, from large-cap blue-chip companies to small-cap startups.
In contrast, the Japanese stock market is dominated by the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE), which is the largest stock exchange in the world by market capitalization. The TSE primarily lists large-cap companies, with a limited number of small and mid-cap stocks.
Investor Sentiment
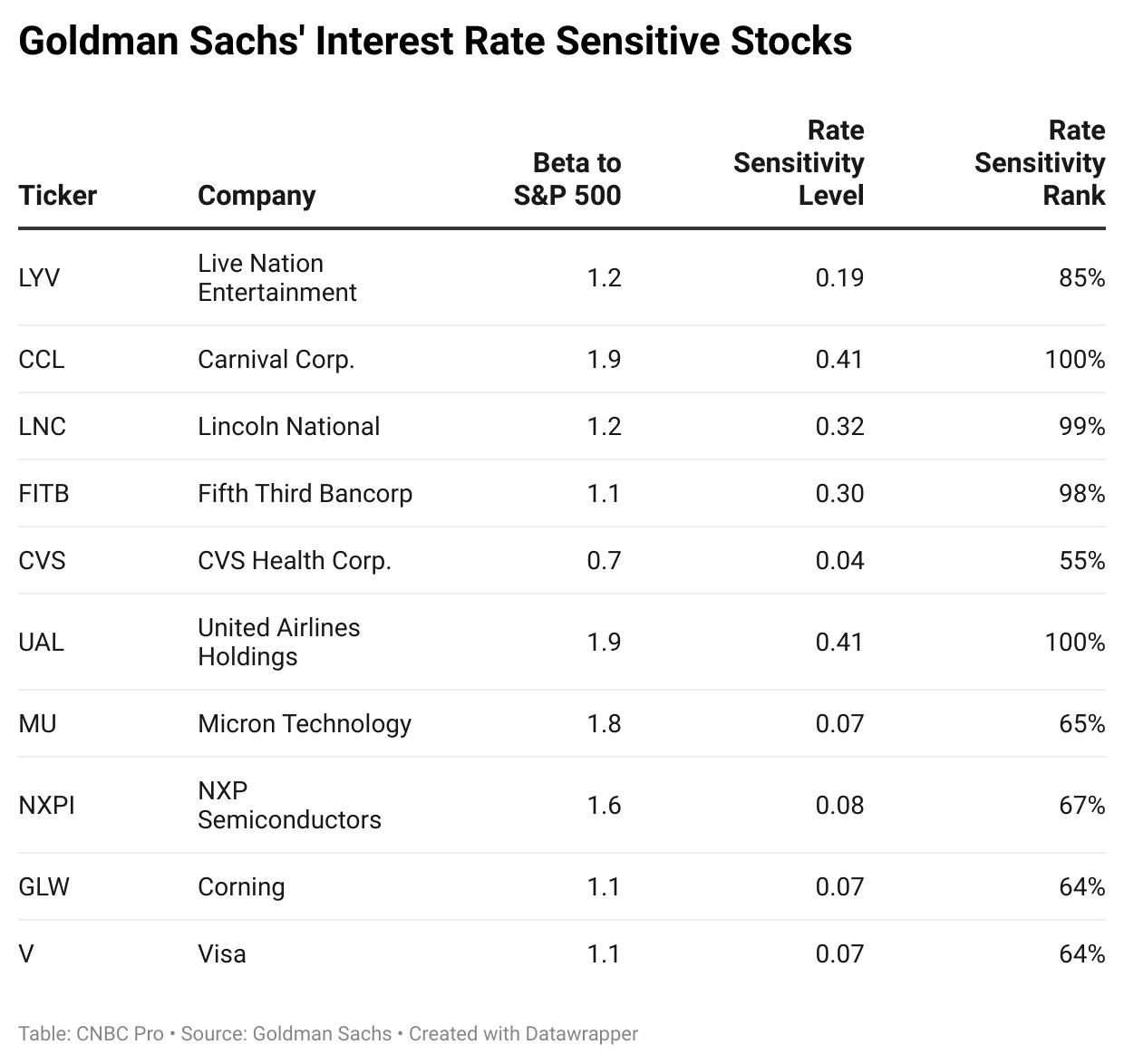
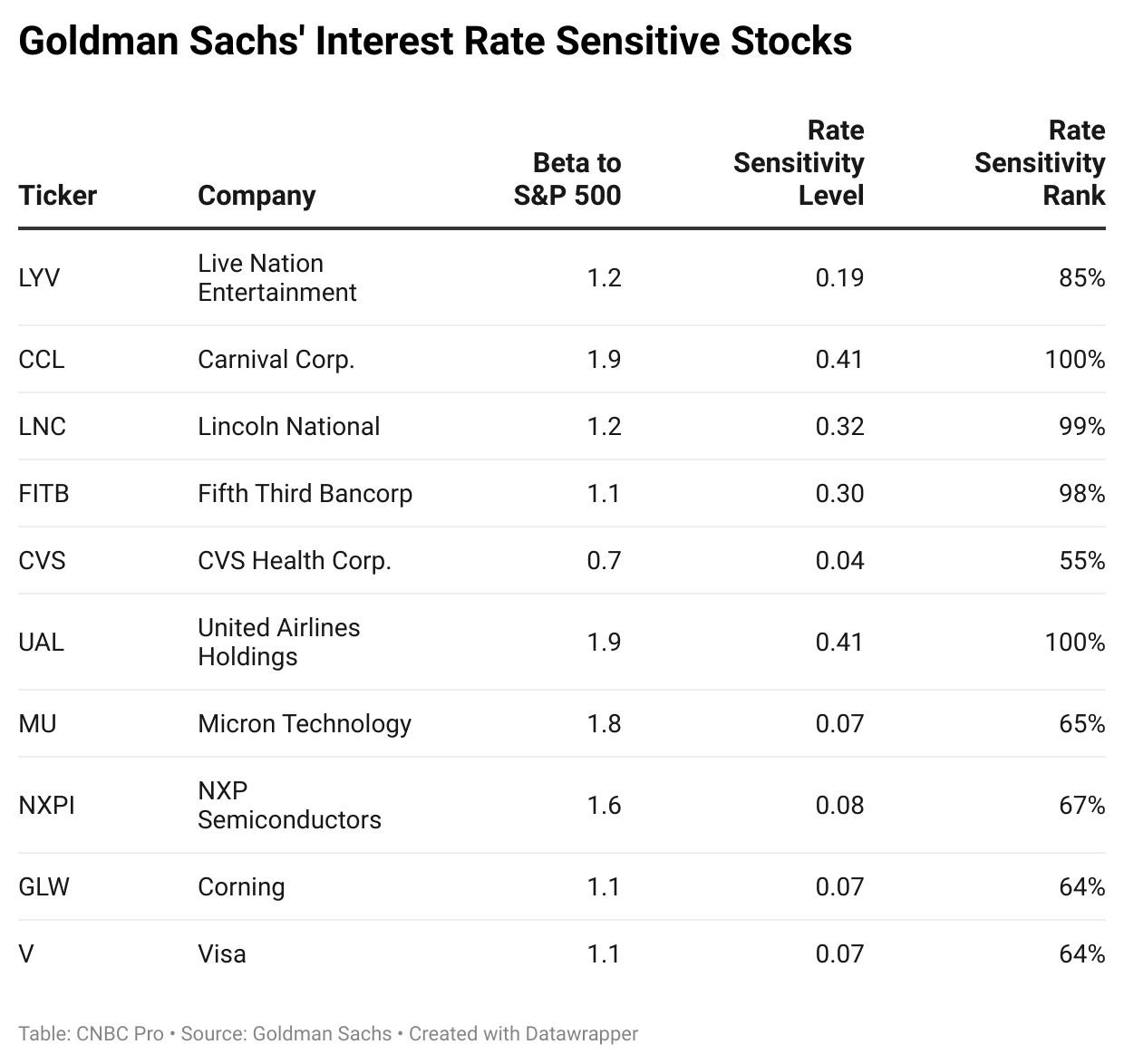
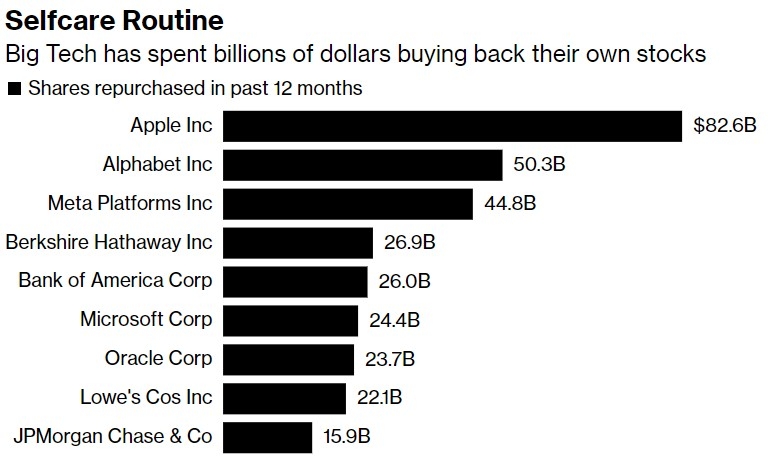
Investor sentiment plays a crucial role in stock market performance. In the US, investors tend to be more speculative and risk-tolerant, often driven by technological advancements and innovation. This sentiment is reflected in the popularity of tech stocks, which have been a major driver of the US stock market's growth.
On the other hand, Japanese investors are generally more conservative and risk-averse. This conservative nature is evident in their preference for stable, dividend-paying stocks, particularly in sectors like consumer goods and manufacturing.
Regulatory Framework
The regulatory framework in the US and Japan also differs significantly. The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees the US stock market, ensuring fair and transparent trading practices. The SEC's stringent regulations have contributed to the market's stability and attractiveness to investors.
In Japan, the Financial Services Agency (FSA) is responsible for regulating the stock market. While the FSA's regulations are also designed to ensure fair trading practices, they may be less stringent compared to those in the US.
Case Studies
To illustrate the differences between the US and Japanese stock markets, let's consider two case studies: Apple Inc. (AAPL) and Toyota Motor Corporation (TM).
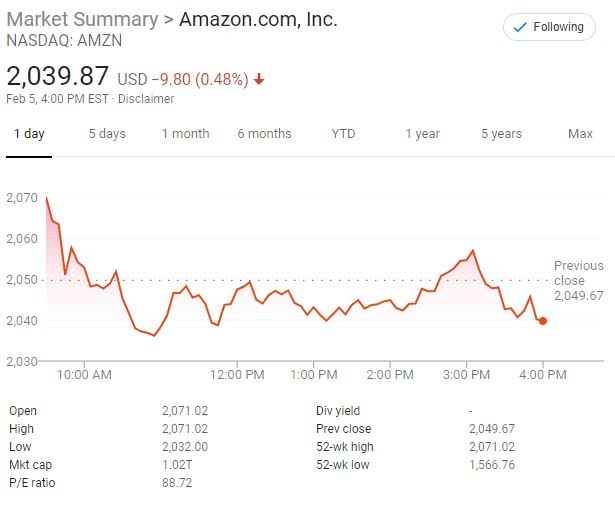
Apple, a US-based company, is listed on the NASDAQ. Its stock has been a major driver of the US stock market's growth, with investors driven by its innovative products and strong financial performance. Apple's stock has seen significant volatility, reflecting the speculative nature of US investors.
Toyota, a Japanese company, is listed on the TSE. Its stock has been a steady performer, offering consistent dividends and stability. Toyota's stock has been less volatile compared to Apple, reflecting the conservative nature of Japanese investors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the US and Japanese stock markets offer distinct opportunities and challenges for investors. Understanding these differences can help investors make informed decisions and capitalize on the strengths of each market. By considering factors like market structure, investor sentiment, and regulatory frameworks, investors can navigate these markets more effectively and achieve their investment goals.
us stock market live