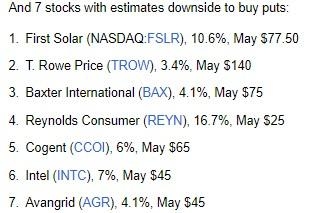
US Government Bonds vs. Common Stock: A Comprehensive Guide
author:US stockS -
In the vast world of investments, understanding the differences between US government bonds and common stock is crucial for making informed decisions. Both are popular investment options, but they cater to different investor profiles and risk appetites. This article delves into the nuances of these two financial instruments, highlighting their features, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Understanding US Government Bonds
US government bonds, often referred to as Treasuries, are issued by the US Department of the Treasury to finance government spending. They are considered one of the safest investments in the world due to the backing of the US government. Key characteristics of US government bonds include:
- Low Risk: As backed by the US government, these bonds are considered risk-free in terms of default.
- Fixed Income: They offer a fixed interest rate, which is paid periodically.
- Liquidity: They are highly liquid, meaning they can be easily bought and sold in the secondary market.
- Long-Term Maturity: Most government bonds have a maturity period of 10 to 30 years.
Understanding Common Stock
Common stock represents ownership in a company. When you purchase common stock, you become a shareholder and have the right to vote on certain corporate decisions. Key features of common stock include:
- Potential for High Returns: Common stock has the potential to offer higher returns compared to government bonds.
- Dividends: Companies may distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends.
- Ownership Rights: Shareholders have voting rights and can participate in the decision-making process of the company.
- Liquidity: Common stocks are also highly liquid, but the market value can be more volatile.
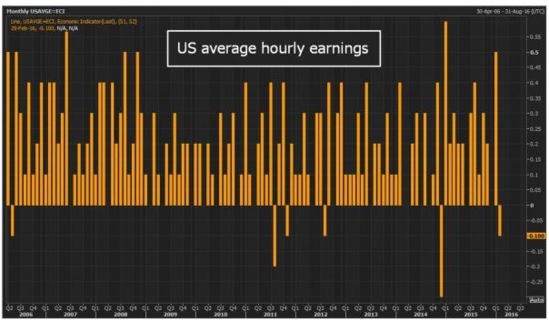
Comparing US Government Bonds and Common Stock
While both US government bonds and common stock have their own set of advantages, they also differ significantly in several aspects:
- Risk: US government bonds are considered low-risk, while common stock is more volatile and carries higher risk.
- Returns: Common stock has the potential for higher returns, but they are not guaranteed.
- Liquidity: Both US government bonds and common stock are highly liquid, but the market value of common stock can be more volatile.
- Investment Goals: US government bonds are ideal for conservative investors seeking stable income, while common stock is suitable for investors with a higher risk tolerance and long-term investment horizon.
Case Study: Apple Inc. (AAPL)
To illustrate the potential of common stock, let's consider the case of Apple Inc. (AAPL). Over the past decade, Apple's stock has seen significant growth, making it one of the most successful investments. In 2010, the stock was trading at around
Conclusion
In conclusion, US government bonds and common stock are two distinct investment options with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these differences is crucial for investors to make informed decisions based on their risk tolerance and investment goals. Whether you prefer the stability of government bonds or the potential for high returns with common stock, both can be valuable components of a well-diversified investment portfolio.
toys r us stocks