Current US Stock Market Valuation Metrics: A Comprehensive Guide
author:US stockS -Valuation(5)Current(35)Market(476)Stock(1759)
The stock market is a dynamic and complex landscape, with various metrics used to evaluate its health and potential for growth. Understanding these metrics is crucial for investors looking to make informed decisions. This article delves into the key valuation metrics currently in use in the US stock market, providing a comprehensive guide for both beginners and seasoned investors.
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio
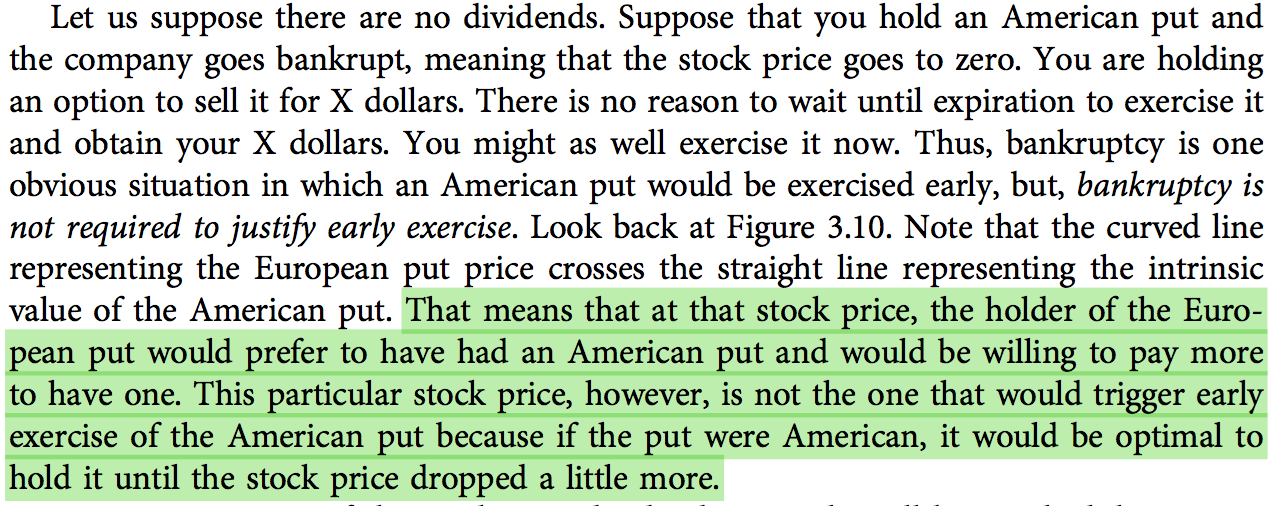
The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio is one of the most popular valuation metrics. It compares the price of a stock to its earnings per share (EPS). A high P/E ratio indicates that investors are willing to pay more for each dollar of earnings, often suggesting that a stock is overvalued. Conversely, a low P/E ratio may indicate that a stock is undervalued.
For example, if a company has a P/E ratio of 20 and its EPS is
Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio
The price-to-book (P/B) ratio compares the market value of a company to its book value. The book value is the company's assets minus its liabilities. A P/B ratio of 1 or less may indicate that a stock is undervalued, while a ratio above 1 suggests the stock might be overvalued.
Consider a company with a P/B ratio of 1.5. If the company's book value is
Earnings Yield
The earnings yield is the inverse of the P/E ratio. It shows the return on investment in terms of earnings. A higher earnings yield indicates a better return on investment.
For instance, if a stock has a P/E ratio of 20, its earnings yield would be 5%. This means that for every dollar invested, an investor can expect a return of 5% based on the company's earnings.
Dividend Yield
The dividend yield measures the return on investment in terms of dividends. It is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the stock's price.
For example, if a stock has a dividend of
Market Capitalization
Market capitalization is the total value of a company's outstanding shares. It is calculated by multiplying the stock price by the number of outstanding shares.
For instance, if a company has 100 million shares outstanding and is trading at
Conclusion
Understanding the various valuation metrics used in the US stock market is essential for making informed investment decisions. By analyzing these metrics, investors can gain insights into the potential value and risks associated with different stocks. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced investor, staying informed about these metrics can help you navigate the complex world of the stock market.
us stock market today